5.1.3 System topology with cellular connectivity using Andruav
This system topology has an onboard smartphone, that connects with the Cockpit-app via cellular networks using the 3rd party software solution Andruav.
Andruav is an Android based software, which can run as 3G endpoint on a smartphone. The smartphone is attached to the aircraft and provides a telemetry link via 3G and the internet.
System topology using Andruav:
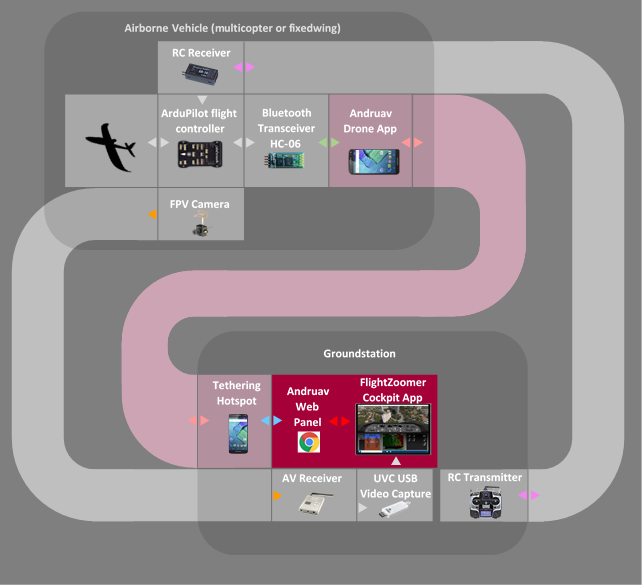
|
What is needed? |
Specifications |
Restriction |
Optional |
|
Airborne Vehicle with ArduPilot flight controller + RC system |
For multicopter: Configured and (auto‑) tuned vehicle, capable to properly fly in Loiter mode |
ArduCopter 3.3 or higher |
Mandatory |
|
For planes: Configured and (auto‑) tuned vehicle, capable to properly fly in Cruise mode. Altitudes should stay within +/- 3…5m |
Arduplane 3.7 or higher |
Mandatory |
|
|
Bluetooth transceiver |
Bluetooth to serial transceiver, |
- |
Mandatory |
|
Device to
run |
Android handset to run the Andruav Drone-app |
|
Mandatory |
|
Tethering hotspot |
Any mobile handset, that can provide internet access via a WiFi hotspot. |
- |
Mandatory |
|
Computer to
run |
The Cockpit-app is a Windows Store app, that runs on any Windows 10 Tablet, Notebook or Desktop computer. Mid- to upper-class performance is preferred. |
Windows 10 Mobile is not supported (as
the screen would |
Mandatory |
|
FPV camera + receiver + UVC video capture |
Any FPV camera and FPV radio transmission product, that can feed its output via a Video-S-to-UVC capture device into the cockpit device. Alternatively, an RTSP source can be configured. |
- |
Optional |
|
Microsoft Surface Dial |
The FlightZoomer autopilot optionally can be controlled with the Microsoft Surface radial controller |
- |
Optional |
Using Direct Link offers the following advantages:
✔ Unlimited range due to cellular network connectivity.
✔ Slightly lower latency of the communication bus.
The following restrictions apply:
Cellular network coverage is needed at the location where the aircraft is flying, and an internet connection is needed where the Cockpit-app runs (which in a typical setup on the field requires a tethering hotspot which in turn means that cellular coverage is required also at the location of the groundstation).
The cellular endpoints need mobile phone contracts (typically 2 are required).
The nature of cellular networks means, that short time communication disruptions can happen at any time and that fail-safe considerations are crucial.